Introduction
Diversification is one of the most important considerations when building an investment portfolio. You may lessen the blow of any one market event by spreading your investments across a wide range of firms, industries, sectors, and asset classes. By spreading out their holdings, investors can reduce their exposure to market fluctuations and enjoy more stable returns. When this happens, Beta becomes very important. One measure of a stock's sensitivity to market fluctuations is its Beta.
Simple math will give you your portfolio's Beta. The fundamental analysis uses Beta to determine how volatile an asset or portfolio is compared to the market as a whole. The market beta is 1.0; hence the degree to which individual stocks deviate from that value is used to assign a relative value to those stocks. You may calculate a security's Beta by knowing the market's standard deviation and the correlation between that security and the market.
What Is Beta?
If the stock's Beta exceeds 1, it will experience larger price swings than the market. If a stock's volatility is less than the market average, its Beta is less than 1.0. High-beta stocks carry a greater risk of loss but offer a greater chance of gain. Low-beta stocks are less risky but typically don't generate as much profit. Since it helps investors determine how much risk they are willing to take for a given return, Beta is widely used as a risk-reward metric. Stock price volatility is an important indicator of overall market risk. When considering risk in terms of the potential loss of value for the underlying stock, Beta can be used as a surrogate for risk.
How Do You Calculate Portfolio Beta?
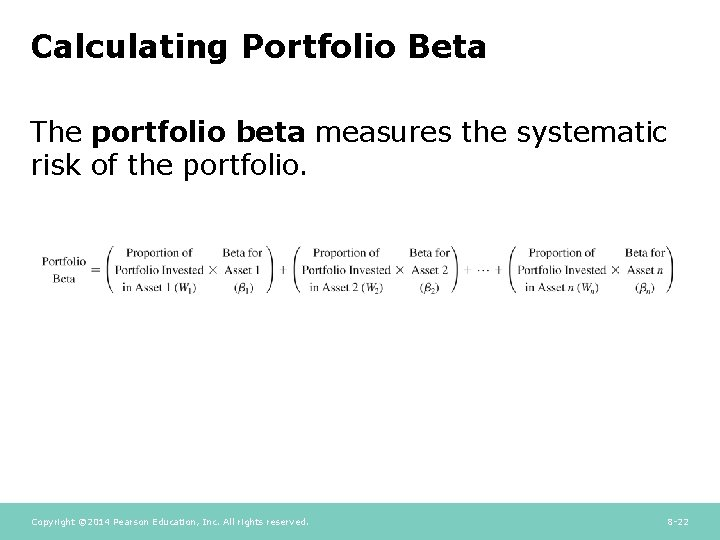
When calculating the Beta of a portfolio, it is always measured against some reference index that the investor has given a value of 1. You are discovering what Beta is helping with the fundamental analysis of stocks. After determining your portfolio's Beta, you can reallocate your holdings to increase or decrease your portfolio's overall risk to meet your financial goals.
Four Ways To Describe Beta
High Beta
Beta values above 1 indicate that the stock is more volatile than the market as a whole. This means that the stock price of a company with a beta of 1.2 relative to the S&P 500 will fluctuate by 20% more than the S&P 500 as a whole. If the S&P 500 rose or fell 10%, the stock price would rise or fall by 12%, respectively. Portfolio beta can be thought of in the same way. High-beta stocks, as predicted by the Modern Portfolio Theory, are more vulnerable to declines but more rewarding during market rallies.
Low Beta
A beta of 0.5 indicates that the stock is 50% less volatile than the market as a whole. Thus, the stock price would shift by 0.5% for every 1% shift in the S&P 500. A stock with less volatility may have a lower potential for gains, but it may also be less likely to see any gains. Despite this fact, investors often prefer stocks with lower volatility. Furthermore, low-Beta investment strategies have shown to generate high returns relative to risk over long periods.
Negative Beta
If a stock or a portfolio has a negative beta, it means it is less stable than the market as a whole. The value of these stocks would decrease if the S&P 500 index rose and increase if the index fell. Gold, for instance, typically moves in the opposite direction of stocks during market turmoil as investors seek safety in its relative stability. Therefore, a portfolio consisting entirely of gold mining companies might have a negative beta.
So-called defensive stocks, such as those of utility companies, often have negative Beta because investors purchase them to hedge against economic volatility. One major drawback of negative Beta is that the expected returns on negative beta assets are typically low, sometimes even lower than the risk-free interest rate.
Zero Beta
An investment's Beta of 0 indicates it has no relationship to the overall market. Some alternative investment firms aim to take no position in the market. To maintain your market neutrality, ignore the performance of indices like the S&P 500.
Conclusion
We hope this is useful and that you'll feel confident calculating the Beta of a portfolio on your own, whether in Excel or by hand. It would help if you considered the risks before placing a trade or investment bet, as anyone who has traded or invested recently knows. Investing in various companies and industries reduces a person's vulnerability to market swings. Beta may not be the best indicator of risk for some stocks because it is based on comparing prices and markets.
To assess the potential danger of a stock, investors must consider the company's fundamentals, earnings, business prospects, and future market for its products or services. Additional risk indicators include the market value of the company's assets, the loan interest rate, and the total amount of debt. If you're going to invest money in stocks, you should do your research and have a strong stomach for risk.



